Implementing AI in the health sector presents challenges such as potential biases in algorithms, race-based discrepancies, limited healthcare data for certain demographics, data privacy and security risks, and inconsistent and inaccurate healthcare data. These challenges can perpetuate healthcare disparities and affect patient outcomes.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!
Credit: blog.creliohealth.com
Challenges Of Implementing AI in The Health Sector
Implementing AI in the health sector faces challenges such as the potential for bias in algorithms and limitations due to the lack of healthcare data for women and minority populations. Additionally, concerns about data privacy and security as well as incomplete and inaccurate healthcare data can impact AI’s effectiveness and perpetuate healthcare disparities.
Concerns About Bias And Lack Of Healthcare Data
One of the major challenges of implementing AI in the health sector is the concern about bias and lack of healthcare data. AI algorithms rely on data to make predictions and decisions, but if the training data has a bias or lacks representation, it can lead to inaccurate and unfair outcomes.
Studies have found race-based discrepancies in AI algorithms, meaning that certain demographic groups may receive unequal treatment or be misdiagnosed. Additionally, there is a lack of healthcare data available for women and minority populations, which further exacerbates the bias.
To ensure that AI in healthcare is effective and fair, it is important to address these concerns by ensuring diverse and representative datasets and implementing measures to mitigate bias.
Advantages And Risks Of AI Usage In Healthcare
While there are challenges in implementing AI in the health sector, it also brings along several advantages and risks. AI has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by improving efficiency, accuracy, and patient outcomes.
Some of the advantages of AI usage in healthcare include:
- Enhanced diagnostics and treatment: AI algorithms can analyze complex medical data and assist doctors in making accurate diagnoses and suggesting personalized treatment plans.
- Improved efficiency: AI can automate repetitive tasks, such as data entry and administrative work, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
- Predictive analytics: AI can help identify patterns and trends in patient data, enabling proactive interventions and preventive care.
However, it is also important to consider the risks associated with AI usage in healthcare:
- Data privacy and security risks: AI relies on vast amounts of sensitive patient data, making it crucial to have strong safeguards in place to protect the privacy and prevent data breaches.
- Bias and fairness concerns: As mentioned earlier, AI algorithms can perpetuate biases and lead to unequal treatment or misdiagnosis of certain demographic groups.
- Liability and regulatory challenges: The implementation of AI in healthcare raises legal and ethical concerns, such as liability for AI-generated decisions and the need for regulatory frameworks to govern its use.
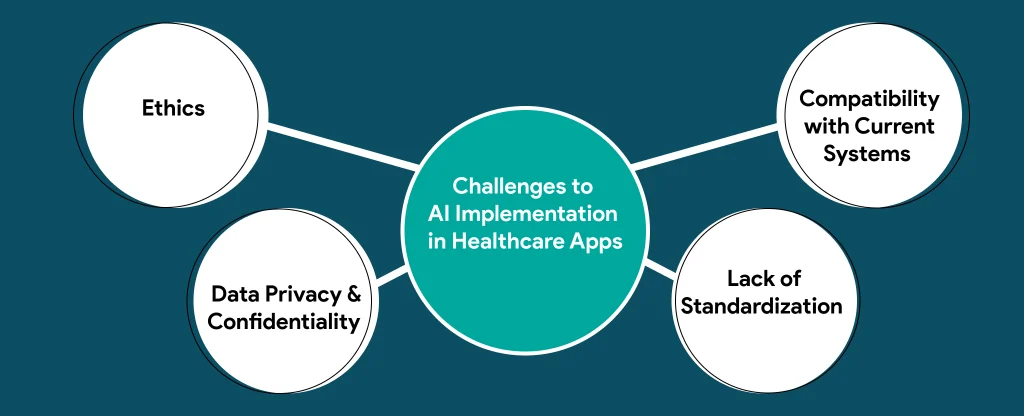
Barriers To The Implementation Of AI in Healthcare
Implementing AI in the healthcare sector is not without its challenges and barriers. Several factors hinder the widespread adoption and implementation of AI in healthcare.
Some of the key barriers include:
- Ethical considerations: The use of AI in healthcare raises ethical questions about patient privacy, consent, and the potential dehumanization of care.
- Technological limitations: AI requires advanced technologies and infrastructure in terms of computing power, data storage, and interoperability, which may not be readily available in all healthcare settings.
- Liability and regulatory concerns: The legal and regulatory landscape for AI in healthcare is still evolving, posing challenges in terms of accountability, transparency, and compliance.
- Workforce implications: The integration of AI in healthcare requires healthcare professionals to acquire new skills and adapt to new roles, which can be a barrier due to resistance to change and training requirements.
- Social acceptance: The widespread adoption of AI in healthcare relies on public trust and acceptance, which may be influenced by concerns about job displacement, privacy, and the potential for AI to replace human judgment.
- Patient safety: The implementation of AI in healthcare must prioritize patient safety and ensure that AI systems are reliable, and accurate, and do not compromise patient well-being.
Overcoming these barriers requires collaboration between healthcare stakeholders, policymakers, and technology experts to address the ethical, technological, regulatory, workforce, social, and patient safety challenges.
Credit: mindster.com
Disadvantages Of AI in The Health Sector
Implementing AI in the health sector is not without its challenges. Concerns include the potential for biased algorithms, discrepancies in data for different populations, and data privacy and security risks. These factors must be carefully considered to ensure the effective and equitable use of AI in healthcare.
Data Privacy And Security Risks
In the healthcare sector, implementing AI poses significant concerns regarding data privacy and security. The generation of vast amounts of sensitive patient data can lead to potential breaches and unauthorized access, threatening patient confidentiality.
Due to the interconnected nature of AI systems, there is always a risk of data theft or leakage, compromising patient privacy. This not only threatens individuals’ rights but also undermines trust in the healthcare system as a whole.
Bias And Fairness Concerns
Another crucial disadvantage of AI in the health sector is the potential for biased and unfair outcomes. AI algorithms rely heavily on the data they are trained on, and if the training data is biased or incomplete, it can lead to unequal treatment and misdiagnosis of certain demographic groups.
This bias can be a result of historical healthcare disparities and inequities, perpetuating existing biases and leading to systemic discrimination. It is essential to address these concerns and ensure that AI systems are trained with diverse and representative data to avoid exacerbating healthcare disparities.
Impact On Healthcare Disparities
The use of AI in healthcare can either help bridge the gap in healthcare disparities or widen it further. It is crucial to ensure that AI implementation does not inadvertently exacerbate existing disparities in healthcare access and outcomes.
If AI systems are not properly calibrated and trained on diverse datasets, it may lead to inaccurate diagnoses or underdiagnosis of certain demographic groups, resulting in unequal healthcare delivery. This undermines the goal of providing equitable care to all individuals, irrespective of factors such as race, gender, or socioeconomic status.
Addressing Challenges In AI Implementation
Implementing AI in the health sector presents a set of challenges that need to be addressed. These challenges include concerns about the effectiveness of AI, potential biases in algorithms, limitations due to lack of healthcare data for certain populations, and the ethical and regulatory barriers to implementation.
Overcoming these challenges is crucial for harnessing the full potential of AI in healthcare.
Improving Healthcare Data Quality And Accuracy
One of the major challenges in implementing AI in the health sector is the quality and accuracy of healthcare data. Healthcare data is frequently incomplete, inconsistent, and inaccurate. This can introduce biases and errors, which can have profound consequences for an AI model trained on such raw data. Biased and inaccurate data can perpetuate healthcare disparities and affect patient outcomes.
Ethical And Regulatory Considerations
Another challenge in implementing AI in healthcare is the ethical and regulatory considerations. With the use of AI, there is a concern about data privacy and security risks, as the generation of vast amounts of sensitive patient data can pose challenges in maintaining confidentiality. Furthermore, there is a need for fairness and transparency in the training data to prevent unequal treatment, misdiagnosis, or underdiagnosis of certain demographic groups.
Collaboration And Knowledge Sharing
Collaboration and knowledge sharing are essential for the successful implementation of AI in the health sector. The healthcare industry needs to foster collaboration between researchers, data scientists, and healthcare providers to share expertise and insights. This can ensure the development of robust AI models and algorithms that can effectively address healthcare challenges. Additionally, knowledge sharing can help in identifying best practices and lessons learned, which can accelerate the implementation and adoption of AI in healthcare.

Credit: www.veritis.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Challenges Of Implementing AI in The Health Sector
What Are The Concerns About AI in Healthcare?
Concerns about AI in healthcare include potential bias in algorithms and limitations due to a lack of data for certain populations. Other concerns are data privacy and security risks, unequal treatment or misdiagnosis based on training data biases and incomplete and inaccurate healthcare data.
What Are The Three Big Challenges Of Artificial Intelligence In Health?
The three big challenges of artificial intelligence in health are bias in algorithms, limited healthcare data for women and minority populations, and concerns about data privacy and security.
What Are The Disadvantages Of AI in the Health Sector?
The disadvantages of AI in the health sector include data privacy and security risks, bias and fairness concerns in training data, and the potential for unequal treatment or misdiagnosis of certain demographic groups. Additionally, inconsistent and inaccurate healthcare data can introduce biases and errors, leading to healthcare disparities and affecting patient outcomes.
What Is The Most Significant Barrier To AI in Healthcare?
The most significant barriers to AI in healthcare are the ethical, technological, liability and regulatory, workforce, social, and patient safety barriers. These barriers include concerns about biases in algorithms, lack of healthcare data for certain populations, data privacy and security risks, and incomplete and inaccurate healthcare data.
Conclusion
Implementing AI in the health sector presents several challenges that need to be addressed. One major concern is the potential for bias in the underlying algorithms, which can result in unequal treatment and misdiagnosis for certain demographic groups. Additionally, the lack of healthcare data for women and minority populations poses limitations and can perpetuate healthcare disparities.
Another challenge is the incomplete, inconsistent, and inaccurate healthcare data, which can introduce biases and errors into AI models. Overcoming these challenges is crucial to ensure the effective and ethical implementation of AI in healthcare.








Comments are closed